Types Of RAM (Random Access Memory) :
RAM(Random Access Memory)
What are the types of RAM?
- DRAM (pronounced DEE-RAM), is widely used as a computer’s main memory. Each DRAM memory cell is made up of a transistor and a capacitor within an integrated circuit, and a data bit is stored in the capacitor. Since transistors always leak a small amount, the capacitors will slowly discharge, causing information stored in it to drain; hence, DRAM has to be refreshed (given a new electronic charge) every few milliseconds to retain data.
- SRAM (pronounced ES-RAM) is made up of four to six transistors. It keeps data in the memory as long as power is supplied to the system unlike DRAM, which has to be refreshed periodically. As such, SRAM is faster but also more expensive, making DRAM the more prevalent memory in computer systems.
What are the common types of DRAM?
-
Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) “synchronizes” the memory speed with CPU clock speed so that the memory controller knows the exact clock cycle when the requested data will be ready. This allows the CPU to perform more instructions at a given time. Typical SDRAM transfers data at speeds up to 133 MHz.
-
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM) takes its name after the company that made it, Rambus. It was popular in the early 2000s and was mainly used for video game devices and graphics cards, with transfer speeds up to 1 GHz.
-
Double Data Rate SDRAM (DDR SDRAM) is a type of synchronous memory that nearly doubles the bandwidth of a single data rate (SDR) SDRAM running at the same clock frequency by employing a method called "double pumping," which allows transfer of data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal without any increase in clock frequency.
-
DDR1 SDRAM has been succeeded by DDR2, DDR3, and most recently, DDR4 SDRAM. Although operating on the same principles, the modules are not backward-compatible. Each generation delivers higher transfer rates and faster performance. The latest DDR4 modules, for example, feature fast transfer rates at 2133/2400/2666and even 3200 MT/s.
What are the types of DRAM packages?
-
Single In-Line Memory Module (SIMM)
SIMM modules were widely used from the late 1980s to 1990s, and are now obsolete. They typically had 32-bit data bus and were available in two physical types—30- and 72-pin. -
Dual In-Line Memory Module (DIMM)
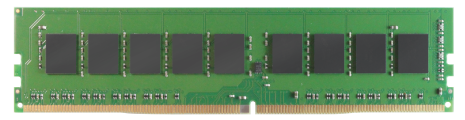
Current memory modules come in DIMMs. "Dual in-line" refers to pins on both sides of the modules. A DIMM originally had a 168-pin connector supporting 64-bit data bus, which is twice the data width of SIMMs. The wider bus means that more data can pass through a DIMM, translating to faster overall performance. Latest DIMMs based on fourth-generation double data rate (DDR4) SDRAM have 288-pin connectors for increased data throughput.
Aside from standard-size DIMMs, are there small form factor DIMMs for space-constrained systems?
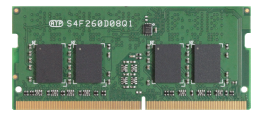
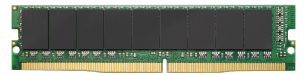
Small outline DIMMs (SO-DIMMs) are the smaller alternatives to DIMMs. While the standard DDR4 DIMM is about 133.35 mm in length, SO-DIMMs are just about half the size of regular DIMMs at 69.6 mm long, making them ideal for ultra-portable devices. Both commonly have a height of 30 mm but may be available in very low profile (VLP) format at 20.3 mm tall or ultra-low profile (ULP) at 17.8 to 18.2 mm. Another type of small form factor DIMM is the Mini-RDIMM, which has a length of only 82 mm compared with 133 mm of regular RDIMMs.
The table below shows ATP's DDR4 DRAM products.
|
DIMM Type |
Size (L x H mm) / Image |
|
DDR4 |
Standard: 133.35 x 31.25
Very Low Profile (VLP): 133.35 x 18.75 |
|
DDR4 |
133.35 x 31.25 |
|
DDR4 |
69.6 x 30
|
|
DDR4 |
Very Low Profile (VLP): 80 x 18.75
|
Table 1. ATP DDR4 DRAM products. (Non-ECC versions are also available.)
The table below shows a size comparison among different types of DRAM modules.
|
DIMM Type |
Size (L x H mm) |
|
|
DDR4 |
Standard |
133.35 x 31.25 |
|
VLP (Very Low Profile) |
133.35 x 18.75 |
|
|
DDR3 |
Standard |
133.35 x 30 |
|
VLP |
133.35 x 18.28 to 18.79 |
|
|
ULP (Ultra-Low Profile) |
133.35 x 17.78 to 18.28 |
|
|
DDR2 |
Standard |
133.35 x 30 |
|
VLP |
133.35 x 18.28 to 18.79 |
|
|
DDR |
Standard |
133.35 x 30 |
|
VLP |
133.35 x 18.28 to 18.79 |
|
|
SDRAM |
Standard |
133.35 x 25.4 to 43.18 |
Table 2. Comparison of DDR4/DDR3/DDR2/DDR dimensions.
Did you know : More than 570 new websites are created every minute.







Etna to my bhi janta hun ram rom ke bare me kuch alag bato
ReplyDelete